我们前面已经分析过 StreamGraph, JobGraph 的生成过程,这两个执行图都是在 client 端生成的。接下来我们将把目光头投向 Flink Job 运行时调度层核心的执行图 - ExecutionGraph。
以此段代码为例,
env.fromData(1, 2, 3, 4).map(line -> line + 1).shuffle().filter(line -> line > 0).print();转换图如下图所示:
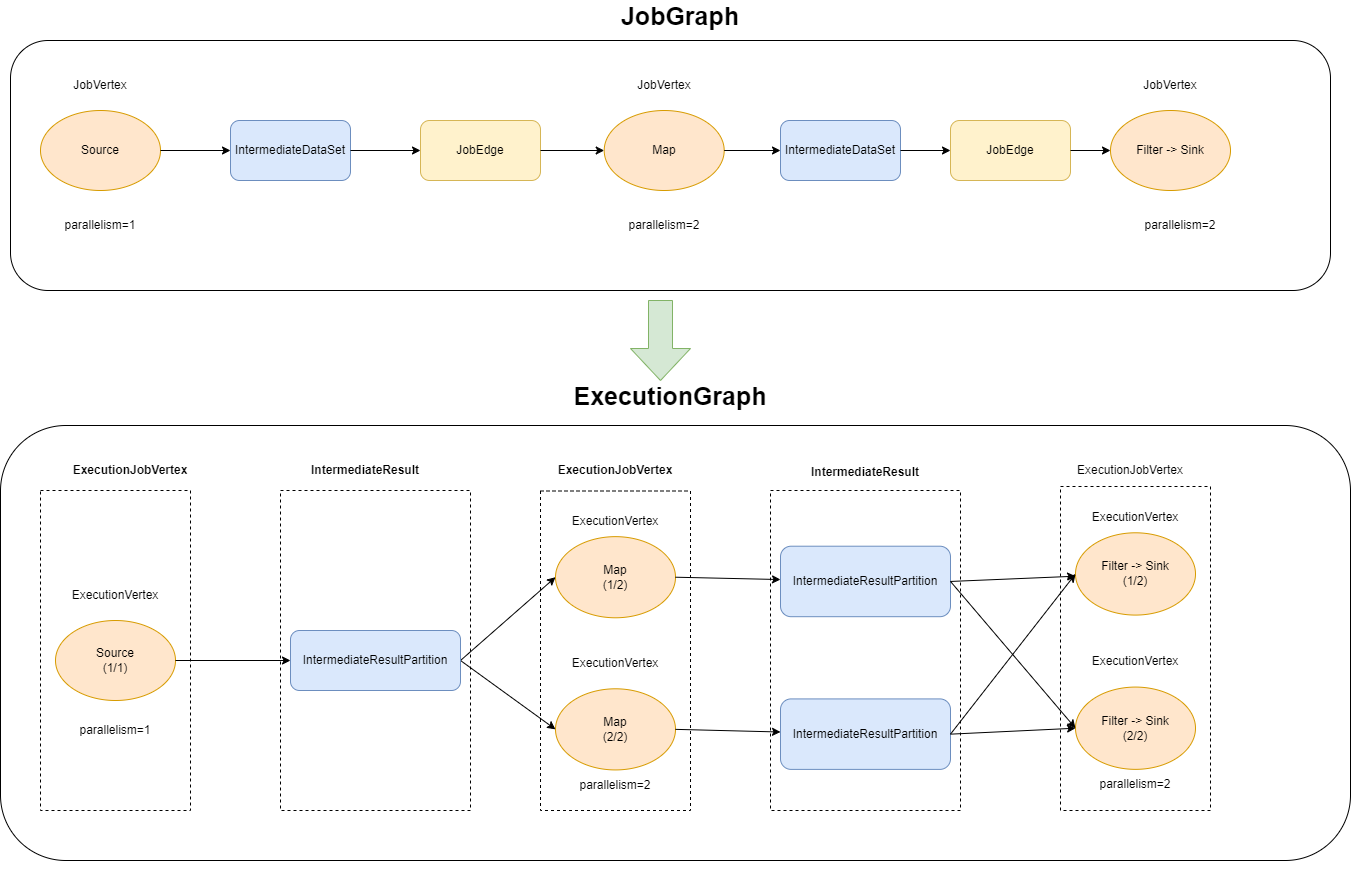
和 StreamGraph 以及 JobGraph 不同的是,ExecutionGraph 是在 JobManager 中生成的。 Client 向 JobManager 提交 JobGraph 后, JobManager 就会根据 JobGraph 来创建对应的 ExecutionGraph,并以此来调度任务。
本文不会介绍 JobMagage 的启动及任务调度过程,后面将会在单独的文章中进行分析。
核心概念※
ExecutionJobVertex※
在 ExecutionGraph 中,节点对应的类是 ExecutionJobVertex,与之对应的就是 JobGraph 中的 JobVertex。每一个 ExexutionJobVertex 都是由一个 JobVertex 生成的。
private final Object stateMonitor = new Object();
private final InternalExecutionGraphAccessor graph;
private final JobVertex jobVertex;
//ExecutionVertex 对应一个并行的子任务
// 算子的并行度是多少,那么就会有多少个
@Nullable private ExecutionVertex[] taskVertices;
// 对外输出
// 对应JobGraph 的IntermediateDataSet
@Nullable private IntermediateResult[] producedDataSets;
@Nullable private List<IntermediateResult> inputs;
private final VertexParallelismInformation parallelismInfo;
private final SlotSharingGroup slotSharingGroup;
@Nullable private final CoLocationGroup coLocationGroup;
@Nullable private InputSplit[] inputSplits;
private final ResourceProfile resourceProfile;
private int numExecutionVertexFinished;
/**
* Either store a serialized task information, which is for all sub tasks the same, or the
* permanent blob key of the offloaded task information BLOB containing the serialized task
* information.
*/
private Either<SerializedValue<TaskInformation>, PermanentBlobKey> taskInformationOrBlobKey =
null;
private final Collection<OperatorCoordinatorHolder> operatorCoordinators;
@Nullable private InputSplitAssigner splitAssigner;
ExecutionVertex※
ExexutionJobVertex 的成员变量中包含一个 ExecutionVertex 数组。我们知道,Flink Job 是可以指定任务的并行度的,在实际运行时,会有多个并行的任务同时在执行,对应到这里就是 ExecutionVertex。ExecutionVertex 是并行任务的一个子任务,算子的并行度是多少,那么就会有多少个 ExecutionVertex。
public static final long NUM_BYTES_UNKNOWN = -1;
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
final ExecutionJobVertex jobVertex;
private final Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, IntermediateResultPartition> resultPartitions;
private final int subTaskIndex;
private final ExecutionVertexID executionVertexId;
//ExecutionVertex的历史执行情况
final ExecutionHistory executionHistory;
private final Time timeout;
/** The name in the format "myTask (2/7)", cached to avoid frequent string concatenations. */
private final String taskNameWithSubtask;
/** The current or latest execution attempt of this vertex's task. */
// 此顶点任务的当前或最新执行尝试。
Execution currentExecution; // this field must never be null
// 输入拆分
final ArrayList<InputSplit> inputSplits;
private int nextAttemptNumber;
private long inputBytes;
/** This field holds the allocation id of the last successful assignment. */
//此字段保存上次成功分配的分配id。
//封装TaskManager的连接信息
@Nullable
private TaskManagerLocation lastAssignedLocation;
//由JobManager通过ResourceManager从TaskManager分配的物理插槽的唯一标识符。
@Nullable
private AllocationID lastAssignedAllocationID;
Execution※
Execution 是对 ExecutionVertex 的一次执行,通过 ExecutionAttemptId 来唯一标识。
private static final int NUM_CANCEL_CALL_TRIES = 3;
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/** The executor which is used to execute futures. */
private final Executor executor;
/** The execution vertex whose task this execution executes. */
private final ExecutionVertex vertex;
/** The unique ID marking the specific execution instant of the task. */
private ExecutionAttemptID attemptId;
/**
* The timestamps when state transitions occurred, indexed by {@link ExecutionState#ordinal()}.
*/
private final long[] stateTimestamps;
/**
* The end timestamps when state transitions occurred, indexed by {@link
* ExecutionState#ordinal()}.
*/
private final long[] stateEndTimestamps;
private final Time rpcTimeout;
private final Collection<PartitionInfo> partitionInfos;
/** A future that completes once the Execution reaches a terminal ExecutionState. */
private final CompletableFuture<ExecutionState> terminalStateFuture;
private final CompletableFuture<?> releaseFuture;
private final CompletableFuture<TaskManagerLocation> taskManagerLocationFuture;
/**
* Gets completed successfully when the task switched to {@link ExecutionState#INITIALIZING} or
* {@link ExecutionState#RUNNING}. If the task never switches to those state, but fails
* immediately, then this future never completes.
*/
private final CompletableFuture<?> initializingOrRunningFuture;
private volatile ExecutionState state = CREATED;
private LogicalSlot assignedResource;
private Optional<ErrorInfo> failureCause =
Optional.empty(); // once an ErrorInfo is set, never changes
/**
* Information to restore the task on recovery, such as checkpoint id and task state snapshot.
*/
@Nullable private JobManagerTaskRestore taskRestore;
/** This field holds the allocation id once it was assigned successfully. */
@Nullable private AllocationID assignedAllocationID;
// ------------------------ Accumulators & Metrics ------------------------
/**
* Lock for updating the accumulators atomically. Prevents final accumulators to be overwritten
* by partial accumulators on a late heartbeat.
*/
private final Object accumulatorLock = new Object();
/* Continuously updated map of user-defined accumulators */
private Map<String, Accumulator<?, ?>> userAccumulators;
private IOMetrics ioMetrics;
private Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, ResultPartitionDeploymentDescriptor>
producedPartitions;
IntermediateResult※
在 JobGraph 中用 IntermediateDataSet 表示 JobVertex 的对外输出,一个 JobGraph 可能有 n(n >=0) 个输出。在 ExecutionGraph 中,与此对应的就是 IntermediateResult。
private final IntermediateDataSet intermediateDataSet;
private final IntermediateDataSetID id;
private final ExecutionJobVertex producer;
private final IntermediateResultPartition[] partitions;
/**
* Maps intermediate result partition IDs to a partition index. This is used for ID lookups of
* intermediate results. I didn't dare to change the partition connect logic in other places
* that is tightly coupled to the partitions being held as an array.
*/
private final HashMap<IntermediateResultPartitionID, Integer> partitionLookupHelper =
new HashMap<>();
private final int numParallelProducers;
private int partitionsAssigned;
private final int connectionIndex;
private final ResultPartitionType resultType;
private final Map<ConsumedPartitionGroup, CachedShuffleDescriptors> shuffleDescriptorCache;
/** All consumer job vertex ids of this dataset. */
private final List<JobVertexID> consumerVertices = new ArrayList<>();由于 ExecutionJobVertex 有 numParallelProducers 个并行的子任务,自然对应的每一个 IntermediateResult 就有 numParallelProducers 个生产者,每个生产者的在相应的 IntermediateResult 上的输出对应一个 IntermediateResultPartition。IntermediateResultPartition 表示的是 ExecutionVertex 的一个输出分区,即:
ExecutionJobVertex --> IntermediateResult
ExecutionVertex --> IntermediateResultPartition一个 ExecutionJobVertex 可能包含多个(n) 个 IntermediateResult, 那实际上每一个并行的子任务 ExecutionVertex 可能会会包含(n) 个 IntermediateResultPartition。
IntermediateResultPartition 的生产者是 ExecutionVertex。
EdgeManager※
通过 EdgeManager将 ExecutionVertex 和 IntermediateResultPartition 连接起来,进而在不同的 ExecutionVertex 之间建立联系。
private final Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumerVertexGroup>> partitionConsumers =
new HashMap<>();
private final Map<ExecutionVertexID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>> vertexConsumedPartitions =
new HashMap<>();
private final Map<IntermediateResultPartitionID, List<ConsumedPartitionGroup>>
consumedPartitionsById = new HashMap<>();
构建 ExecutionGraph 的流程※
创建 ExecutionGraph 的入口在 org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.DefaultExecutionGraphBuilder#buildGraph 中。
// 构建入口
public static DefaultExecutionGraph buildGraph(
JobGraph jobGraph,
Configuration jobManagerConfig,
ScheduledExecutorService futureExecutor,
Executor ioExecutor,
ClassLoader classLoader,
CompletedCheckpointStore completedCheckpointStore,
CheckpointsCleaner checkpointsCleaner,
CheckpointIDCounter checkpointIdCounter,
Time rpcTimeout,
BlobWriter blobWriter,
Logger log,
ShuffleMaster<?> shuffleMaster,
JobMasterPartitionTracker partitionTracker,
TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.PartitionLocationConstraint partitionLocationConstraint,
ExecutionDeploymentListener executionDeploymentListener,
ExecutionStateUpdateListener executionStateUpdateListener,
long initializationTimestamp,
VertexAttemptNumberStore vertexAttemptNumberStore,
VertexParallelismStore vertexParallelismStore,
Supplier<CheckpointStatsTracker> checkpointStatsTrackerFactory,
boolean isDynamicGraph,
ExecutionJobVertex.Factory executionJobVertexFactory,
MarkPartitionFinishedStrategy markPartitionFinishedStrategy,
boolean nonFinishedHybridPartitionShouldBeUnknown,
JobManagerJobMetricGroup jobManagerJobMetricGroup)
throws JobExecutionException, JobException {
checkNotNull(jobGraph, "job graph cannot be null");
final String jobName = jobGraph.getName();
final JobID jobId = jobGraph.getJobID();
final JobType jobType = jobGraph.getJobType();
//设置作业信息
final JobInformation jobInformation =
new JobInformation(
jobId,
jobType,
jobName,
jobGraph.getSerializedExecutionConfig(),
jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(),
jobGraph.getUserJarBlobKeys(),
jobGraph.getClasspaths());
final int executionHistorySizeLimit =
jobManagerConfig.get(JobManagerOptions.MAX_ATTEMPTS_HISTORY_SIZE);
final PartitionGroupReleaseStrategy.Factory partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory =
PartitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactoryLoader.loadPartitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory(
jobManagerConfig);
final int offloadShuffleDescriptorsThreshold =
jobManagerConfig.get(
TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.OFFLOAD_SHUFFLE_DESCRIPTORS_THRESHOLD);
final TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory;
try {
taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory =
new TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory(
BlobWriter.serializeAndTryOffload(jobInformation, jobId, blobWriter),
jobId,
partitionLocationConstraint,
blobWriter,
nonFinishedHybridPartitionShouldBeUnknown,
offloadShuffleDescriptorsThreshold);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new JobException("Could not create the TaskDeploymentDescriptorFactory.", e);
}
// create a new execution graph, if none exists so far
//创建新的执行图 (如果到目前为止不存在)
final DefaultExecutionGraph executionGraph =
new DefaultExecutionGraph(
jobGraph.getJobType(),
jobInformation,
futureExecutor,
ioExecutor,
rpcTimeout,
executionHistorySizeLimit,
classLoader,
blobWriter,
partitionGroupReleaseStrategyFactory,
shuffleMaster,
partitionTracker,
executionDeploymentListener,
executionStateUpdateListener,
initializationTimestamp,
vertexAttemptNumberStore,
vertexParallelismStore,
isDynamicGraph,
executionJobVertexFactory,
jobGraph.getJobStatusHooks(),
markPartitionFinishedStrategy,
taskDeploymentDescriptorFactory);
// set the basic properties
try {
executionGraph.setJsonPlan(JsonPlanGenerator.generatePlan(jobGraph));
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.warn("Cannot create JSON plan for job", t);
// give the graph an empty plan
executionGraph.setJsonPlan("{}");
}
// initialize the vertices that have a master initialization hook
// file output formats create directories here, input formats create splits
final long initMasterStart = System.nanoTime();
log.info("Running initialization on master for job {} ({}).", jobName, jobId);
for (JobVertex vertex : jobGraph.getVertices()) {
String executableClass = vertex.getInvokableClassName();
if (executableClass == null || executableClass.isEmpty()) {
throw new JobSubmissionException(
jobId,
"The vertex "
+ vertex.getID()
+ " ("
+ vertex.getName()
+ ") has no invokable class.");
}
try {
//JobVertex 在 Master 上进行初始化
vertex.initializeOnMaster(
new SimpleInitializeOnMasterContext(
classLoader,
vertexParallelismStore
.getParallelismInfo(vertex.getID())
.getParallelism()));
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId,
"Cannot initialize task '" + vertex.getName() + "': " + t.getMessage(),
t);
}
}
log.info(
"Successfully ran initialization on master in {} ms.",
(System.nanoTime() - initMasterStart) / 1_000_000);
// topologically sort the job vertices and attach the graph to the existing one
//对作业顶点进行拓扑排序,并将图附加到现有的
//对所有的 Jobvertext 进行拓扑排序,并生成 ExecutionGraph 内部的节点和连接
List<JobVertex> sortedTopology = jobGraph.getVerticesSortedTopologicallyFromSources();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(
"Adding {} vertices from job graph {} ({}).",
sortedTopology.size(),
jobName,
jobId);
}
executionGraph.attachJobGraph(sortedTopology, jobManagerJobMetricGroup);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug(
"Successfully created execution graph from job graph {} ({}).", jobName, jobId);
}
// configure the state checkpointing
if (isDynamicGraph) {
// dynamic graph does not support checkpointing so we skip it
log.warn("Skip setting up checkpointing for a job with dynamic graph.");
} else if (isCheckpointingEnabled(jobGraph)) {
//配置状态检查点
JobCheckpointingSettings snapshotSettings = jobGraph.getCheckpointingSettings();
// load the state backend from the application settings
final StateBackend applicationConfiguredBackend;
final SerializedValue<StateBackend> serializedAppConfigured =
snapshotSettings.getDefaultStateBackend();
if (serializedAppConfigured == null) {
applicationConfiguredBackend = null;
} else {
try {
applicationConfiguredBackend =
serializedAppConfigured.deserializeValue(classLoader);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId, "Could not deserialize application-defined state backend.", e);
}
}
final StateBackend rootBackend;
try {
rootBackend =
StateBackendLoader.fromApplicationOrConfigOrDefault(
applicationConfiguredBackend,
jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(),
jobManagerConfig,
classLoader,
log);
} catch (IllegalConfigurationException | IOException | DynamicCodeLoadingException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId, "Could not instantiate configured state backend", e);
}
// load the checkpoint storage from the application settings
//从应用程序设置加载检查点存储
final CheckpointStorage applicationConfiguredStorage;
final SerializedValue<CheckpointStorage> serializedAppConfiguredStorage =
snapshotSettings.getDefaultCheckpointStorage();
if (serializedAppConfiguredStorage == null) {
applicationConfiguredStorage = null;
} else {
try {
applicationConfiguredStorage =
serializedAppConfiguredStorage.deserializeValue(classLoader);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId,
"Could not deserialize application-defined checkpoint storage.",
e);
}
}
final CheckpointStorage rootStorage;
try {
rootStorage =
CheckpointStorageLoader.load(
applicationConfiguredStorage,
rootBackend,
jobGraph.getJobConfiguration(),
jobManagerConfig,
classLoader,
log);
} catch (IllegalConfigurationException | DynamicCodeLoadingException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId, "Could not instantiate configured checkpoint storage", e);
}
// instantiate the user-defined checkpoint hooks
//实例化用户定义的检查点钩子
final SerializedValue<MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory[]> serializedHooks =
snapshotSettings.getMasterHooks();
final List<MasterTriggerRestoreHook<?>> hooks;
if (serializedHooks == null) {
hooks = Collections.emptyList();
} else {
final MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory[] hookFactories;
try {
hookFactories = serializedHooks.deserializeValue(classLoader);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new JobExecutionException(
jobId, "Could not instantiate user-defined checkpoint hooks", e);
}
final Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
final ClassLoader originalClassLoader = thread.getContextClassLoader();
thread.setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
try {
hooks = new ArrayList<>(hookFactories.length);
for (MasterTriggerRestoreHook.Factory factory : hookFactories) {
hooks.add(MasterHooks.wrapHook(factory.create(), classLoader));
}
} finally {
thread.setContextClassLoader(originalClassLoader);
}
}
final CheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration chkConfig =
snapshotSettings.getCheckpointCoordinatorConfiguration();
executionGraph.enableCheckpointing(
chkConfig,
hooks,
checkpointIdCounter,
completedCheckpointStore,
rootBackend,
rootStorage,
checkpointStatsTrackerFactory.get(),
checkpointsCleaner,
jobManagerConfig.get(STATE_CHANGE_LOG_STORAGE));
}
return executionGraph;
}
小结※
本文简单概括了 ExecutionGraph 涉及到的概念和其生成过程。
到目前为止,我们了解了 StreamGraph, JobGraph 和 ExecutionGraph 的生成过程,以及他们内部的节点和连接的对应关系。总的来说, StreamGraph 是最原始的,更贴近用户逻辑的 DAG 执行图;JobGraph 是对 StreamGraph 的进一步优化,将能够合并的算子合并为一个节点以降低运行时数据传输的开销;ExecutionGraph 则是作业运行是用来调度的执行图,可以看作是并行化版本的 JobGraph,将 DAG 拆分到基本的调度单元。
参考资料:

